Describe the Difference Between Classical and Empirical Probability
The classical method of computing probabilities does not require that a probability experiment actually be performed. View Notes - Week 4 Discussion 2 from MAT 126 at Ashford University.

Solved 5 1 59 Question Help Describe The Difference Between Chegg Com
Classical probability refers to a probability that is based on formal reasoning.

. Shake and empty bag of coins 10 times and tally up how many head and tails are showing. In your own words describe two main differences between classical and empirical probabilities. So in classical probability you think of the space of the outcomes and try to find an abstract reason to assign the probability we used mathematics logic to came up with the number of possibilities and the one of outcomes.
Empirical probabilities have to have been performed. For example if three coin tosses yielded a head the empirical probability of getting a head in a coin toss is 100. You do not need more than that.
You will need an even number of coins any denomination between 16 and 30. 2 Gather 16 to 30 coins. In theoretical probability we assume that the probability of occurrence of any event is equally likely and based on that we predict the probability of an event.
You will need an even number of coins any denomination between 16 and 30. The second difference is that classical probability assumes the occurrence of any possible event within the sample space is just a likely as any other where empirical probability makes no assumptions. Classical Empirical Subjective and Axiomatic.
Classical or theoretical probability is the ration of the number of outcomes of an event to the total number of outcomes in the sample space. Furthermore they can be also differentiated as classical probability as the probability of certain events that is already. Discussion 1 The purpose of this Discussion is to analyze a financial plan that portrays a somewhat typical budgeting scheme.
The classical method of computing probabilities does not require that a probability experiment actually be performed. It is measured between 0 and 1 inclusive. The classical method of computing probabilities does not require that a probability experiment actually be O B.
The empirical method acquired information to approximate the empirical data by conducting a probability experimentHowever the classical method does not conduct probability experiment rather it relies on counting technique and requires equally likely outcome. The empirical method of. Demonstrate your understanding of the similarities and differences between classical probability and empirical probability.
Up to 20 cash back In your own words describe two main differences between classical and empirical probabilities. Describe the difference between classical and empirical probability. The empirical method obtains an exact empirical probability of an event by conducting a probability experiment.
Empirical or Experimental probability. For example if you flip a fair coin the probabili. In your own words describe two main differences between classical and empirical probabilities.
Classical sometimes called A priori or Theoretical This is the perspective on probability that most people first encounter in formal education although they may encounter the subjective perspective in informal education. Rather it relies on counting techniques and requires equally likely outcomes. Experimental or empirical probability is the probability of an event based on the results of an actual experiment conducted several times.
So if an event is unlikely to occur its probability is 0 whereas 1 indicates the certainty for the occurrence. 3 Write the. The classical method obtains an exact probability of an event by conducting a probability experiment.
The empirical method obtains an approximate probability of. In the empirical definition on the other hand you dont think you just do experiments and count. 2 Gather 16 to 30 coins.
The key difference is the role of information. The classical method of computing probabilities does not require that a probability experiment actually be performed. Math - Classical and Empirical Probabilities.
If the probability of an event is high it is more likely that the event will happen. The empirical method of computing empirical probabilities does not require that a probability experiment actually be performed. Rather it relies on counting techniques and requires equally likely outcomes.
Describe two main differences between classical and empirical probabilities. Classical and Empirical Probabilities 1 Describe two main differences between classical and empirical probabilities. Classical Empirical Subjective Probability Empirical Probability Classical Probability observes the number of occurrences through experimentation calculates probability from a relative frequency distribution through the equation.
Rather it relies on counting techniques and requires equally likely outcomes. When we toss an unbiased coin the chances of occurrence of head. After 100 experiments you gathered empirical evidence that head occurred more often than.
You do not need more than that. 1 Describe two main differences between classical and empirical probabilities. Answer 1 of 3.
Empirical Probability Vs Theoretical Probability. The classical method obtains an exact probability of an event by conducting a probability experiment. The empirical method obtains an approximate empirical probability of an event by conducting a probability experiment.
Put all of the coins in a small bag or container big enough to allow the coins to be shaken. The empirical method obtains an approximate empirical. Get started for FREE Continue.
Classical probabilities are based on. Gather coins you find around your home or in your pocket or purse. Classical probability assumes that certain outcomes are equally likely while empirical probability relies on actual experience to determine the likelihood of outcomes.
The first difference between the two is that classical probability is a theoretical computation whereas empirical probability is computed based on experiment or observation. Uncategorized Describe the difference between classical and empirical probability. Empirical probabilities are based on observations.
Empirical probability refers to a probability that is based on historical data. Rather it relies on counting techniques and requires equally likely outcomes. Classical probabilities are based on assumptions.
In your own words describe two main differences between classical and empirical probabilities. Two main differences between classical and empirical probability are. Four perspectives on probability are commonly used.
The empirical method obtains an approximate empirical probability of an event by conducting a probability experiment. The empirical method obtains an approximate empirical probability of an event by conducting a probability experiment. Subjective Probability We know the number of.
Gather coins you find around your home or in your pocket or purse. Classical probability is used when each in a sample space is equally likely to occur. Classical probabilities do not require an action to take place.
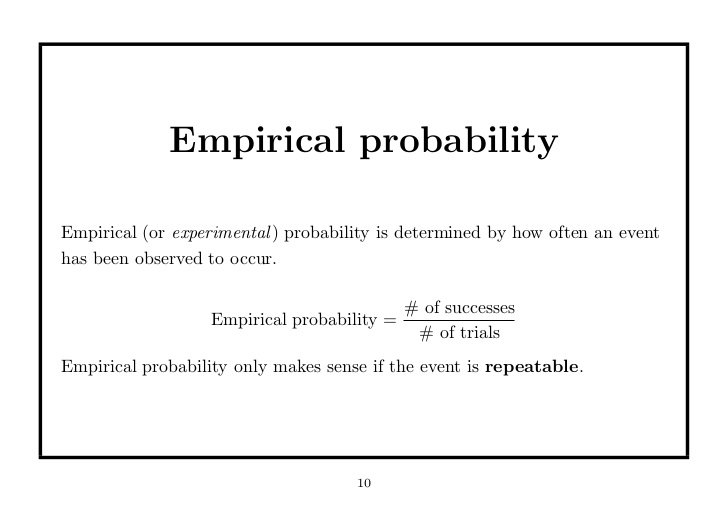
Classical And Empirical Probability Indiafreenotes

What Are The Definitions Of Classical Probability Empirical Probability And Subjective Probability Quora

What Are The Definitions Of Classical Probability Empirical Probability And Subjective Probability Quora
Comments
Post a Comment